If you need urgent consulting help click here
Pico-Pi i.MX7D - Android Things IoT Development Platform
Overview
The i.MX7D SoC is a Hybrid multi-core processor composed of Single Cortex A7 core and Single Cortex M4 core. Zephyr was ported to run on the M4 core. In a later release, it will also communicate with the A7 core (running Linux) via RPmsg.
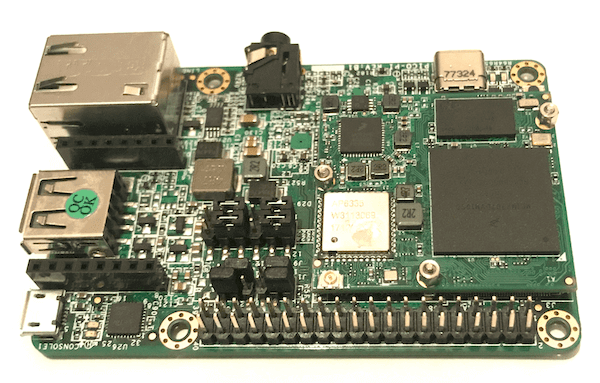
Hardware
The Pico-Pi Platform is composed of a CPU and IO board.
Pico-Pi IO Board
S1 - On/Off (MX7_ONOFF signal)
Board to board connector : Edison compatible connector (70 configurable pins)
mikroBUS expansion connector ADC, GPIO, I²C, PWM, SPI, UART)
10-pin needle JTAG Connector
Debug USB exposing One UART
MIPI DSI 1 lane Connector
LCD Touch Connector
Audio Jack: Mic and Stereo Headphone
Pico-Pi CPU Board
CPU i.MX7 Dual with a Single Cortex A7 (1 GHz) core and Single Cortex M4 (200MHz) core
Memory
RAM -> A7: 4GB
RAM -> M4: 3x32KB (TCML, TCMU, OCRAM_S), 1x128KB (OCRAM) and 1x256MB (DDR)
Flash -> A7: 8GB eMMC
For more information about the i.MX7 SoC and Pico-Pi i.MX7D, see these references:
Supported Features
The Pico-Pi i.MX7D configuration supports the following hardware features on the Cortex M4 Core:
Interface |
Controller |
Driver/Component |
|---|---|---|
NVIC |
on-chip |
nested vector interrupt controller |
SYSTICK |
on-chip |
systick |
GPIO |
on-chip |
gpio |
I2C |
on-chip |
i2c |
UART |
on-chip |
serial port-polling; serial port-interrupt |
The default configuration can be found in the defconfig file:
boards/arm/pico_pi_m4/pico_pi_m4_defconfig
Other hardware features are not currently supported by the port.
Connections and IOs
The Pico-Pi board Board was tested with the following pinmux controller configuration.
Board Name |
SoC Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
UART_TX232 |
UART1_TX |
UART Console |
UART_RX232 |
UART1_RX |
UART Console |
RX_E |
UART6_TX |
UART (mikroBUS and Edison) |
TX_E |
UART6_RX |
UART (mikroBUS and Edison) |
I2CX_SDA_3V |
I2C1_SDA |
I2C (mikroBUS and Edison) |
I2CX_SCL_3V |
I2C1_SCL |
I2C (mikroBUS and Edison) |
System Clock
The M4 Core is configured to run at a 200 MHz clock speed.
Serial Port
The iMX7D SoC has seven UARTs. The number 6 is configured for the console and the number 2 is used in the mikroBUS connector.
Programming and Debugging
The Pico-Pi i.MX7D doesn’t have QSPI flash for the M4 and it needs to be started by the A7 core. The A7 core is responsible to load the M4 binary application into the RAM, put the M4 in reset, set the M4 Program Counter and Stack Pointer, and get the M4 out of reset. The A7 can perform these steps at bootloader level or after the Linux system has booted.
The M4 can use up to 5 different RAMs. These are the memory mapping for A7 and M4:
Region |
Cortex-A7 |
Cortex-M4 (System Bus) |
Cortex-M4 (Code Bus) |
Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
DDR |
0x80000000-0xFFFFFFFF |
0x80000000-0xDFFFFFFF |
0x10000000-0x1FFEFFFF |
2048MB (less for M4) |
OCRAM |
0x00900000-0x0091FFFF |
0x20200000-0x2021FFFF |
0x00900000-0x0091FFFF |
128KB |
TCMU |
0x00800000-0x00807FFF |
0x20000000-0x20007FFF |
32KB |
|
TCML |
0x007F8000-0x007FFFFF |
0x1FFF8000-0x1FFFFFFF |
32KB |
|
OCRAM_S |
0x00180000-0x00187FFF |
0x20180000-0x20187FFF |
0x00000000-0x00007FFF |
32KB |
References
i.MX 7 Dual Reference Manual from page 182 (section 2.1.2 and 2.1.3)
At compilation time you have to choose which RAM will be used. This
configuration is done in the file boards/arm/pico_pi_m4/pico_pi_m4.dts with
“zephyr,flash” (when CONFIG_XIP=y) and “zephyr,sram” properties. The available
configurations are:
"zephyr,flash"
- &ddr_code
- &tcml_code
- &ocram_code
- &ocram_s_code
- &ocram_pxp_code
- &ocram_epdc_code
"zephyr,sram"
- &ddr_sys
- &tcmu_sys
- &ocram_sys
- &ocram_s_sys
- &ocram_pxp_sys
- &ocram_epdc_sys
Below you will find the instructions to load and run Zephyr on M4 from A7 using u-boot.
Connect both micro USB interfaces into the PC. This is the A7 console and the UART6 in the Edison connector is M4 console for Zephyr with both configured to work at 115200 8N1. The USB interface is used to power the CPU and IO boards and is connected to the USB OTG interface of the i.MX7D.
After powering up the platform stop the u-boot execution on the A7 core and
expose the eMMC as mass storage with the following command in the u-boot
prompt: ums 0 mmc 0. Copy the compiled zephyr.bin to the first FAT
partition and remove the mounted device on the PC by issuing a “Ctrl+C” in the
u-boot prompt.
Set the u-boot environment variables and run the zephyr.bin from the
appropriated memory configured in the Zephyr compilation:
setenv bootm4 'fatload mmc 0:1 $m4addr $m4fw && dcache flush && bootaux $m4addr'
# TCML
setenv m4tcml 'setenv m4fw zephyr.bin; setenv m4addr 0x007F8000'
setenv bootm4tcml 'run m4tcml && run bootm4'
run bootm4tcml
# TCMU
setenv m4tcmu 'setenv m4fw zephyr.bin; setenv m4addr 0x00800000'
setenv bootm4tcmu 'run m4tcmu && run bootm4'
run bootm4tcmu
# OCRAM
setenv m4ocram 'setenv m4fw zephyr.bin; setenv m4addr 0x00900000'
setenv bootm4ocram 'run m4ocram && run bootm4'
run bootm4ocram
# OCRAM_S
setenv m4ocrams 'setenv m4fw zephyr.bin; setenv m4addr 0x00180000'
setenv bootm4ocrams 'run m4ocrams && run bootm4'
run bootm4ocrams
# DDR
setenv m4ddr 'setenv m4fw zephyr.bin; setenv m4addr 0x80000000'
setenv bootm4ddr 'run m4ddr && run bootm4'
run bootm4ddr
Building an Application and Run an Application for more details).
